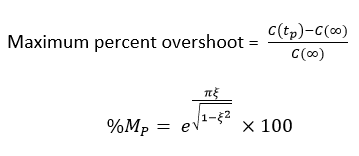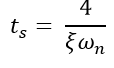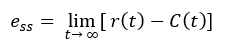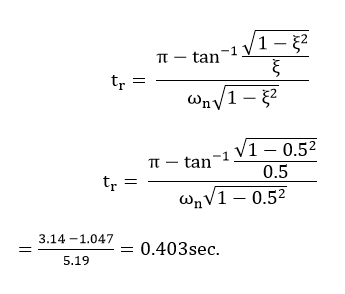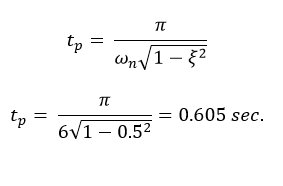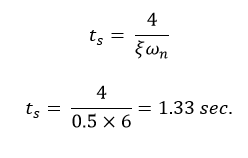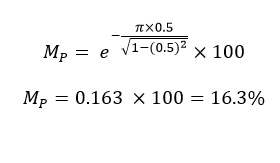Time domain specifications | Delay Time | Rise Time | Peak Time | Maximum Peak | Settling Time | Steady State error | control system
Time Domain Specifications:
All the time domain specifications are represented in this figure. The response up to the settling time is known as transient response and the response after the settling time is known as steady state response.
Following are the common transient response characteristics:
1. Delay Time.
2. Rise Time.
3. Peak Time.
4. Maximum Peak.
5. Settling Time.
6. Steady State error.
Delay Time:
The time required for the response to reach 50% of the final value in the first time is called the delay time.
Rise Time:
The time required for response to rising from 10% to 90% of final value, for an overdamped system and 0 to 100% for an underdamped system is called the rise time of the system.
Peak Time:
The time required for the response to reach the 1st peak of the time response or 1st peak overshoot is called the Peak time.
Maximum overshoot:
The difference between the peak of 1st time and steady output is called the maximum overshoot. It is defined by
Settling Time (ts):
The time that is required for the response to reach and stay within the specified range (2% to 5%) of its final value is called the settling time.
Steady State Error (ess):
The difference between actual output and desired output as time't' tends to infinity is called the steady state error of the system.
When a second-order system is subjected to a unit step input, the values of ξ = 0.5 and ωn = 6 rad/sec. Determine the rise time, peak time, settling time and peak overshoot.
Solution:
Given-
ξ = 0.5 ω n = 6 rad/sec
Rise Time:
Peak time:
Settling Time:
Maximum overshoot:
Labels: Control System, Delay Time, Maximum Peak, Peak Time, Rise Time, Settling Time, Steady State error, Time domain specifications